4.8 Soft Tissue
4.8.1 Soft Tissue
- There are 4 types of soft tissue of interest to this course:
- Muscle
- Tendon
- Ligament
- Cartilage
- We will introduce each of these in this lecture, and each will get substantial treatment (lecture+)
4.8.2 Muscle

- Approximately 700 muscles in the human body
- Three broad classifications
- Skeletal
- Cardiac
- Smooth and visceral (internal to the body cavity)
- Also can be classified as
- Voluntary Striated (skeletal)
- Involuntary Striated (cardiac)
- Involuntary (smooth)
4.8.3 Muscle groups
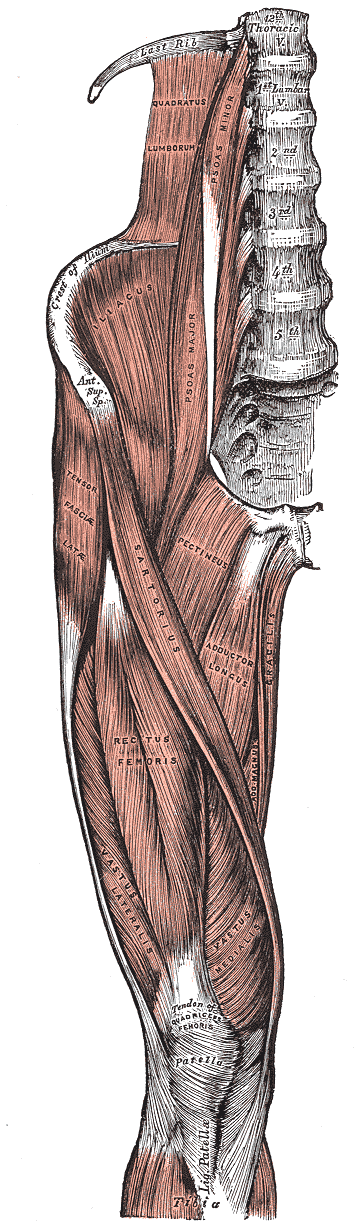
@Gray1918
- In this course, we are principally concerned with skeletal muscles
- These muscles predominately act in groups that have a common insertion point on a bone
- The groups act in concert to provide motion and stability… we
will most often consider the group as a whole
- ie the quadriceps is made up of four muscles
- Muscles groups contract to activate, position, and stabilize the body
- They work in concert with each other, co-contraction of
agonist and antagonist muscles produces joint
control and stability
- Example, the hamstring and quadriceps simultaneously contract by variable amounts to stability the knee joint in flexion/extension

Unlabelled Image Missing
- Muscle contraction leads to forces, forces leads to strains in the
muscle
- Thus, the muscle is also a spring which stores energy
- This is important for energy management within the body
- Note the distinction between strain (injury) and strain (elasticity)
4.8.4 Tendons and ligaments

- Tendons connect muscle to bone
- Ligaments connect bone to bone
- Both can be modeled as simple cables, however, each has tissue bundles at multiple length scales (ie like fibers that join to form a strand, strands join to form a rope)
- When stretched, they deform and have spring like qualities as well
4.8.5 Articular cartilage
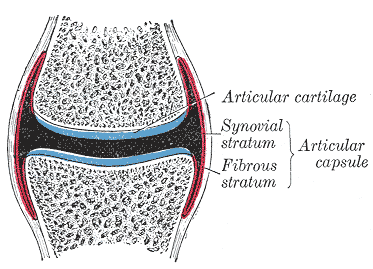
- Complex set of tissues consisting of fibrous matrix, water, large molecules, and other elements
- 2-4 mm thick… thickness changes with age
- Note: bursae - Tiny, slippery sacs of fluid which facilitate this gliding motion by providing a thin cushion and reducing friction between surfaces.10
4.8.6

Elbow joint - deep dissection (anterior view, human cadaver) Anatomist90 CCSA3.0
- No nerves or blood supply in cartilage
- Difficult to detect damage
- Does not heal
- Level of detail in the engineering model depends on the desired outcome