3.2 Conceptual Overview of Orthopaedic Biomechanics
(Reading assignment: [@Bartel2006] Chapter 1.
3.2.1 The human body as a machine
- The human body is a machine!
- A combination of rigid and resistant bodies
- Bones and the soft tissue associated with them
- Links are joints which have low friction and transfer large forces
- Large, precise and imprecise motion
- Performs useful work
- A combination of rigid and resistant bodies
Contrasting humans with most machines
- Most joints have imprecisely defined motion
- There is flexibility in the soft tissues (ligaments, muscles)
- This flexibility leads to coupling between loads and motion:
- i.e. the motion can effect the loads in ways that do not typically occur in “conventional” machines
- Changes in force will produce changes in joint motion,
- Changes in relative position between bones (at joint) will change the forces in the joints
- “sloppy joint”
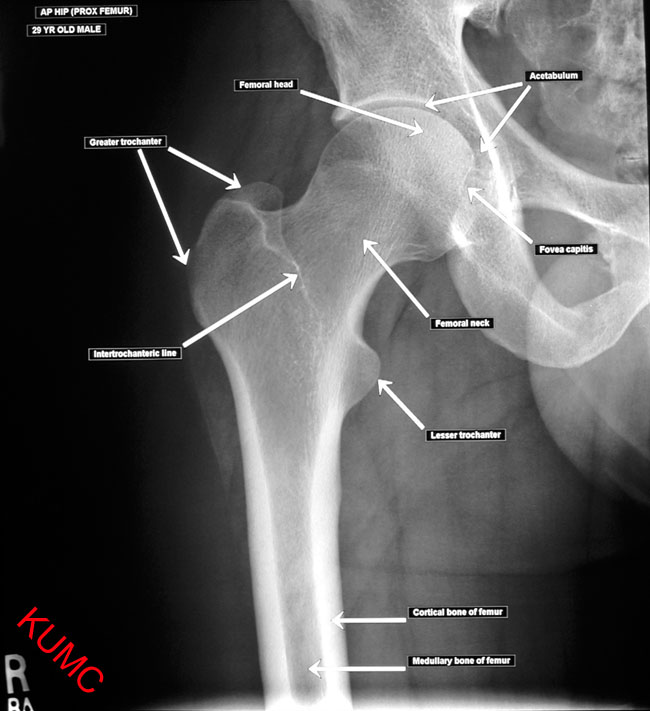
Joints, range of motion and, precision
- Hip joint
- is more rigidly defined by its bony ball and socket
- widely varying soft tissue restraint… but less reliance
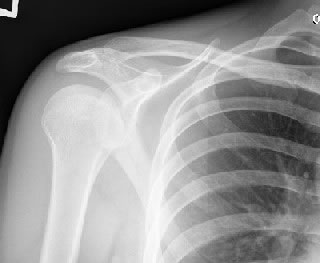
- Shoulder joint
- is very imprecisely defined with its ball and socket
- widely varying soft tissue restraint…
- requires more soft-tissue control and precision placement
Unlabelled Image Missing
“Osteoporosis is the leading cause of age-related kyphosis, with sarcopenia, or age-related muscle loss, being a secondary cause,” Patel explains.2
- Skeletal loads vary from person to person and over time in a particular person
- Aging and disease change skeletal response
- We are not often concerned about precise loads, stresses, etc,
- rather we compute approximate loads within a level of uncertainty
- We seek to describe the fundamental behavior of the system
- Use engineering methods to understand the effect of damage and disease
- Predict, understand, and influence the methods and techniques used to restore function
- The skeleton has an amazing ability to repair damage and adapt to physical demands
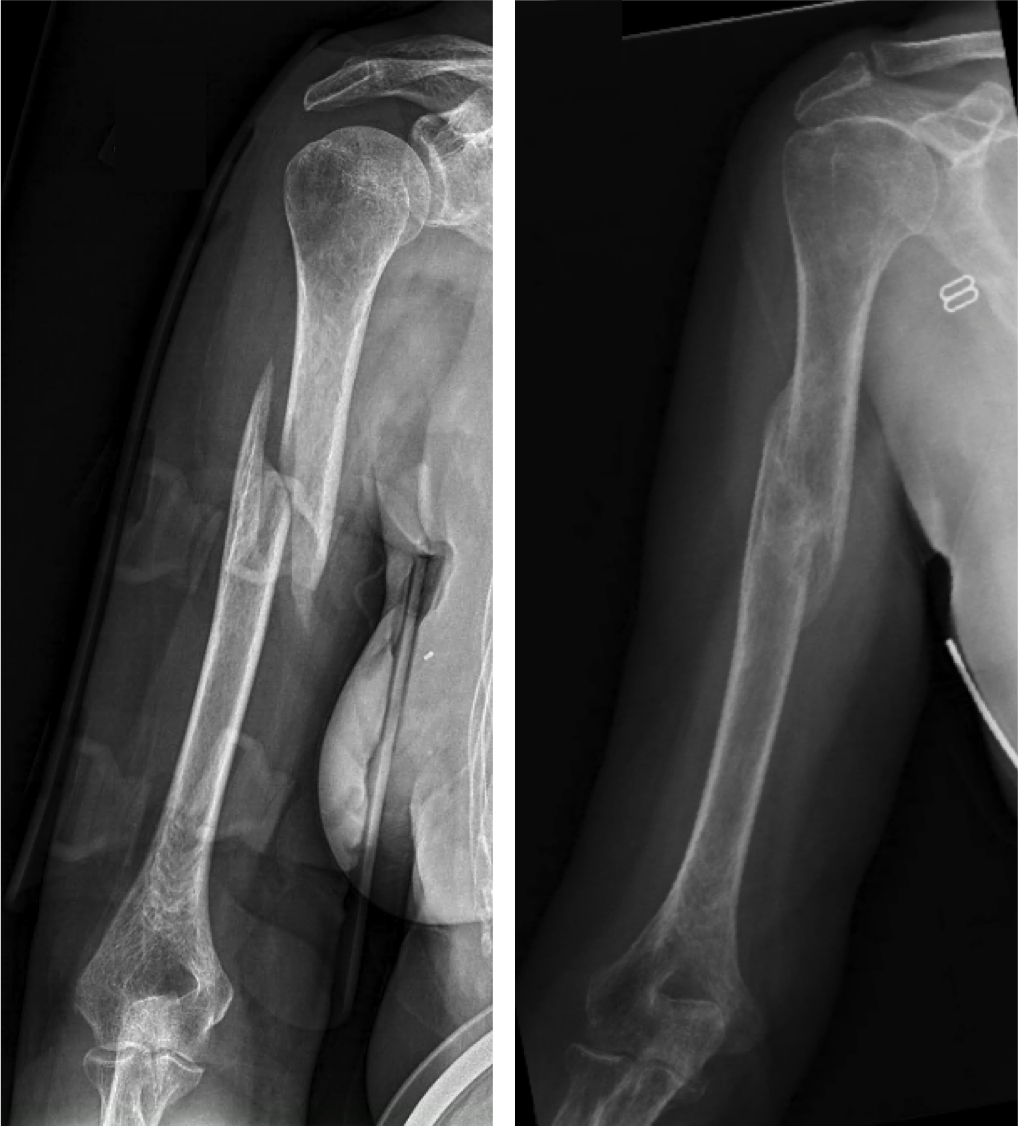
Non-surgical treatment with a brace. Many humerus fractures can be treated without surgery. The humerus shaft fracture above was successfully treated in a “Sarmiento brace”, which wraps around the upper arm and holds the bone aligned while it heals.4