4.12 Visualizing orthopaedic structures
4.12.1 X-Ray of a Hand
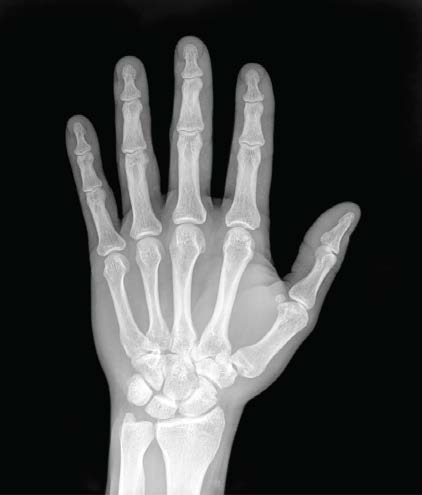
@OpenStaxAnatomy2020 Ch. 1
High energy electromagnetic radiation allows the internal structures of the body, such as bones, to be seen in X-rays like these. (credit: Trace Meek/flickr)
(slide credit: @OpenStaxAnatomy2020 Ch. 1)
4.12.2 Computed Tomography Scan

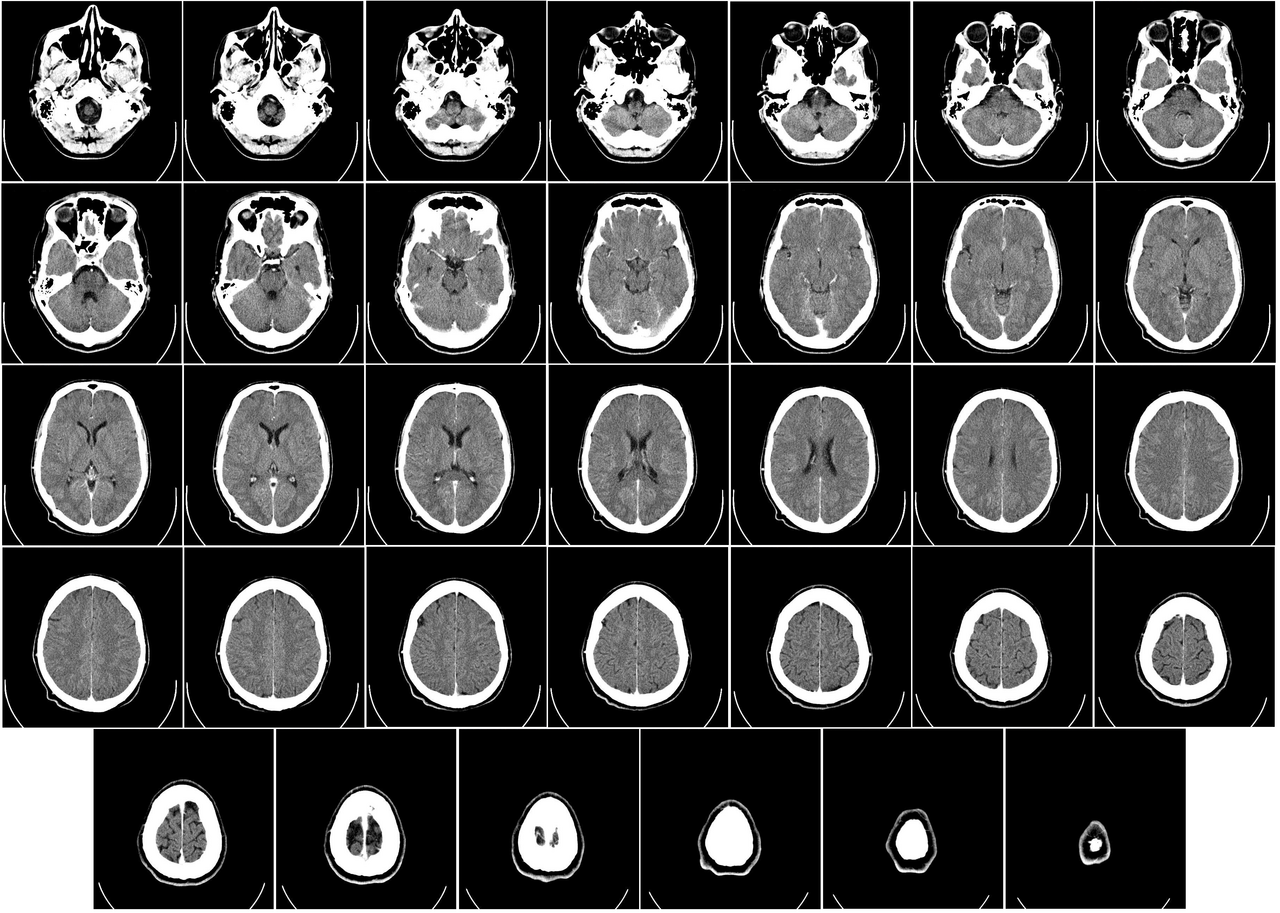
- The results of a CT scan of the head are shown as successive transverse sections.
- Uses ionizing radiation (x-ray radiation)
- Higher contrast visualization of bony structures
4.12.3 Magnetic Resonance Imaging


- An MRI machine generates a magnetic field around a patient.
- Higher contrast visualization of soft tissues
4.12.4 Ultrasound

Unlabelled Image Missing
Ultrasonography is a totally safe noninvasive imaging technique. In contrast to computed tomography (CT) and X-rays, it does not emit ionizing radiation. Unlike magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), it is safe for all patients, including those with cardiac pacemakers and metal implants, without any contraindications.
@Blankstein2011
4.12.5 Ultrasound in orthpaedics
- Can be high resolution
- Can offer real time assessment (i.e., patient can move, image is dynamic)
- Sometimes referred to as the “orthopedic surgeon’s stethoscope”
- Detection of tendon tears, tiny calcifications, and foreign bodies
4.12.6 Positron emission tomography
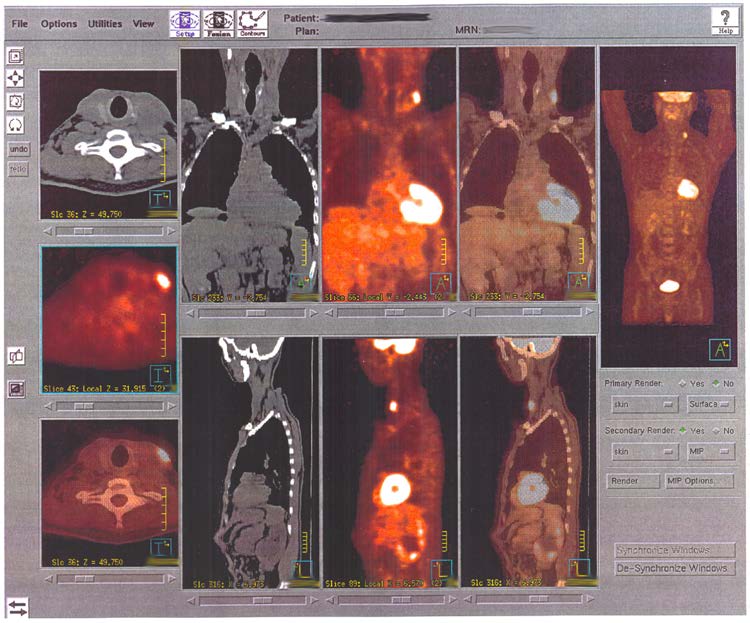
@OpenStaxAnatomy2020 Ch. 2
PET highlights areas in the body where there is relatively high glucose use, which is characteristic of cancerous tissue. This PET scan shows sites of the spread of a large primary tumor to other sites.
(slide credit: @OpenStaxAnatomy2020 Ch. 2)

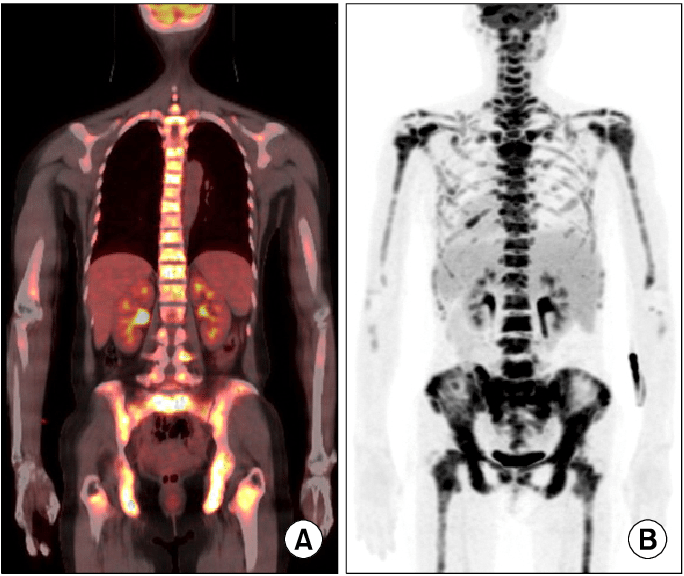
- Can be used to track bone forming activity